Review of Regional Haze Situation for September 2025
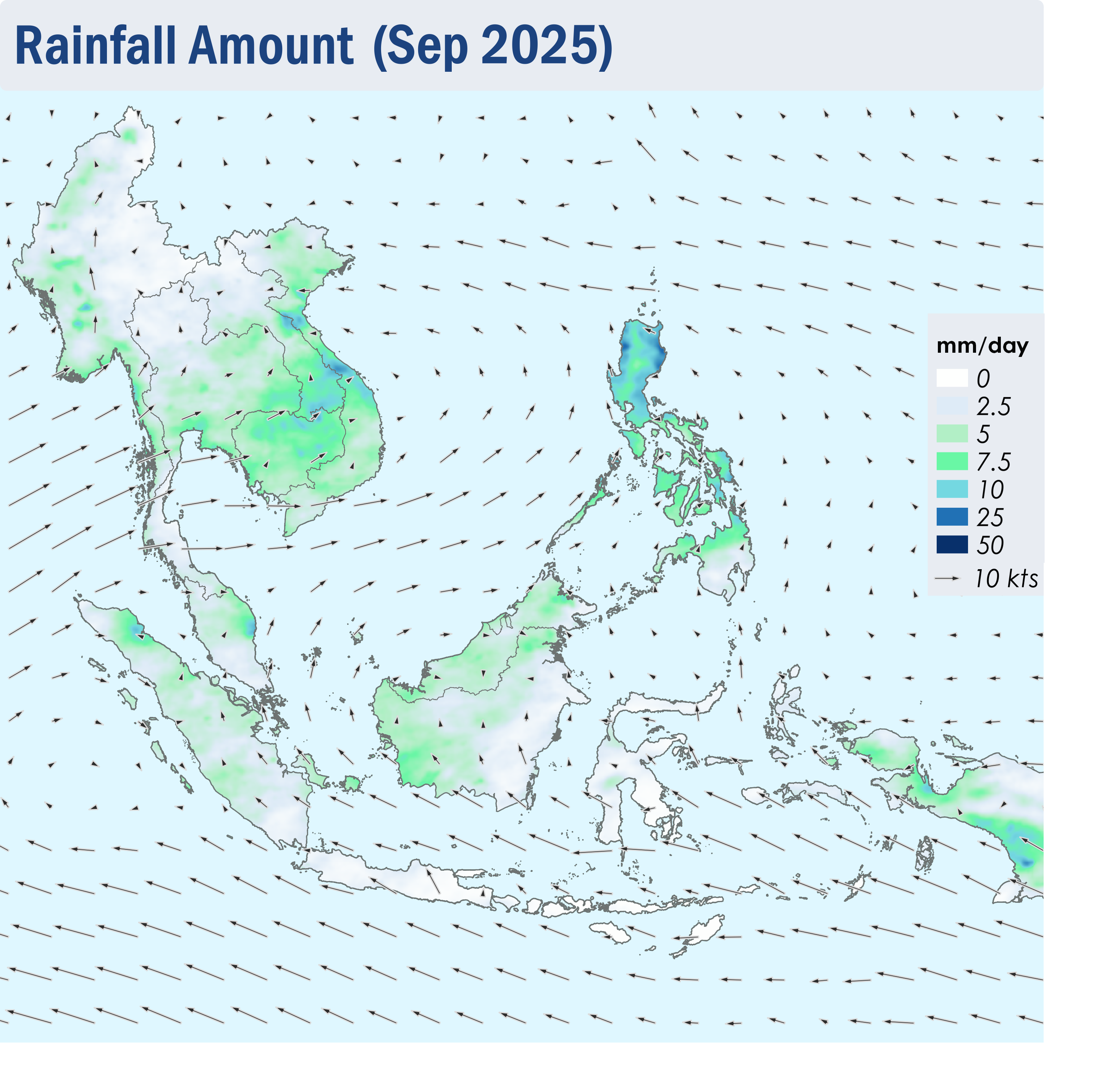
1.1 Southwest monsoon conditions persisted over the ASEAN region in September 2025. The prevailing low-level winds blew mainly from the southeast over areas south of the Equator and turned to blow from the southwest or west over areas north of the Equator (Figure 1).
1.2 While Java and the Lesser Sunda Islands continued to face drier conditions, showers were prevalent over the rest of the ASEAN region. There were three notable tropical cyclones during the review period, namely Tropical Storm Mitag , Super Typhoon Ragasa and Typhoon Bualoi, which developed one after another in September. Heavy rains and strong winds brought by the storms affected several areas in the northern ASEAN region, particularly the Philippines and the eastern parts of the Mekong sub-region, where several floods and landslides were reported.
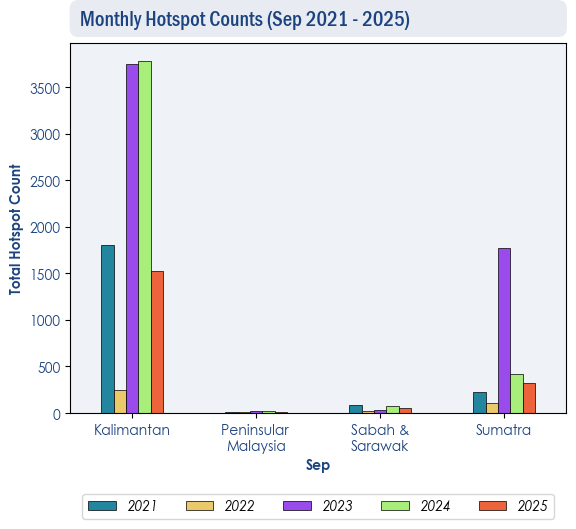
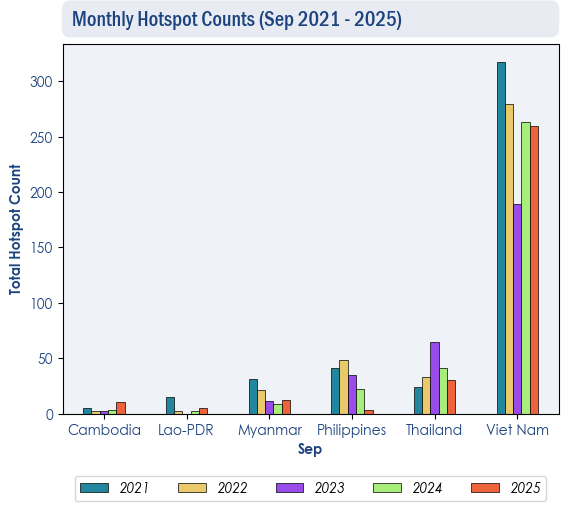
1.3 The hotspot counts for the ASEAN region in September 2025 were generally lower than or comparable to those recorded in the same month during previous years. (Figures 2 and 3).
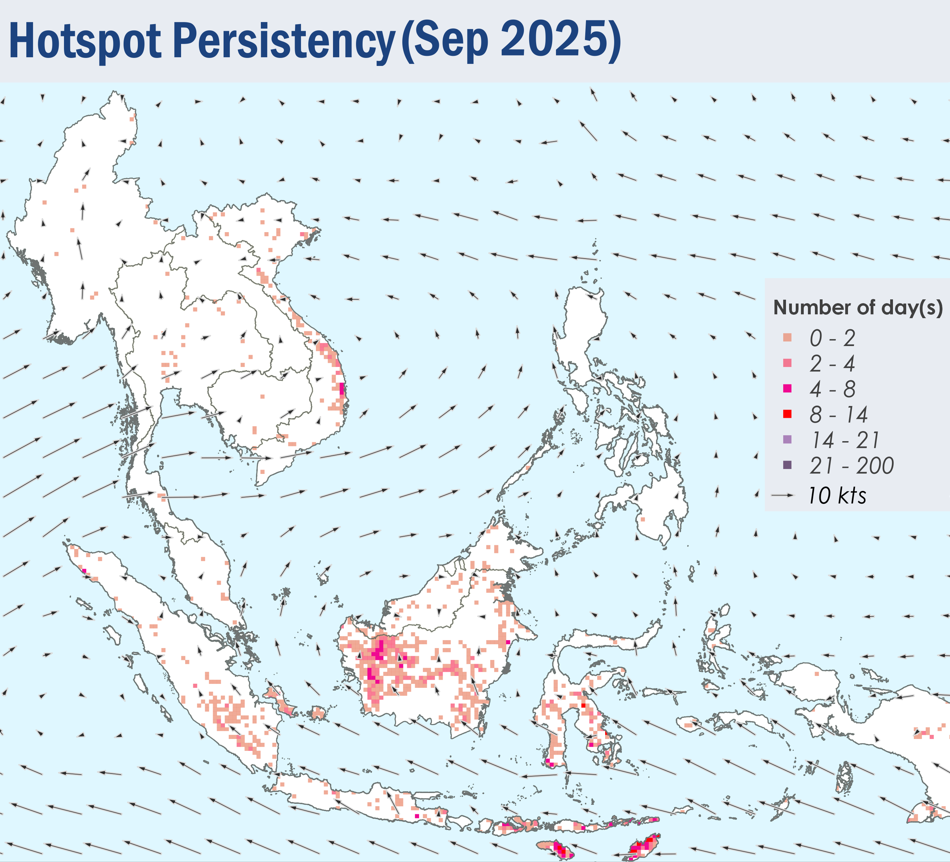
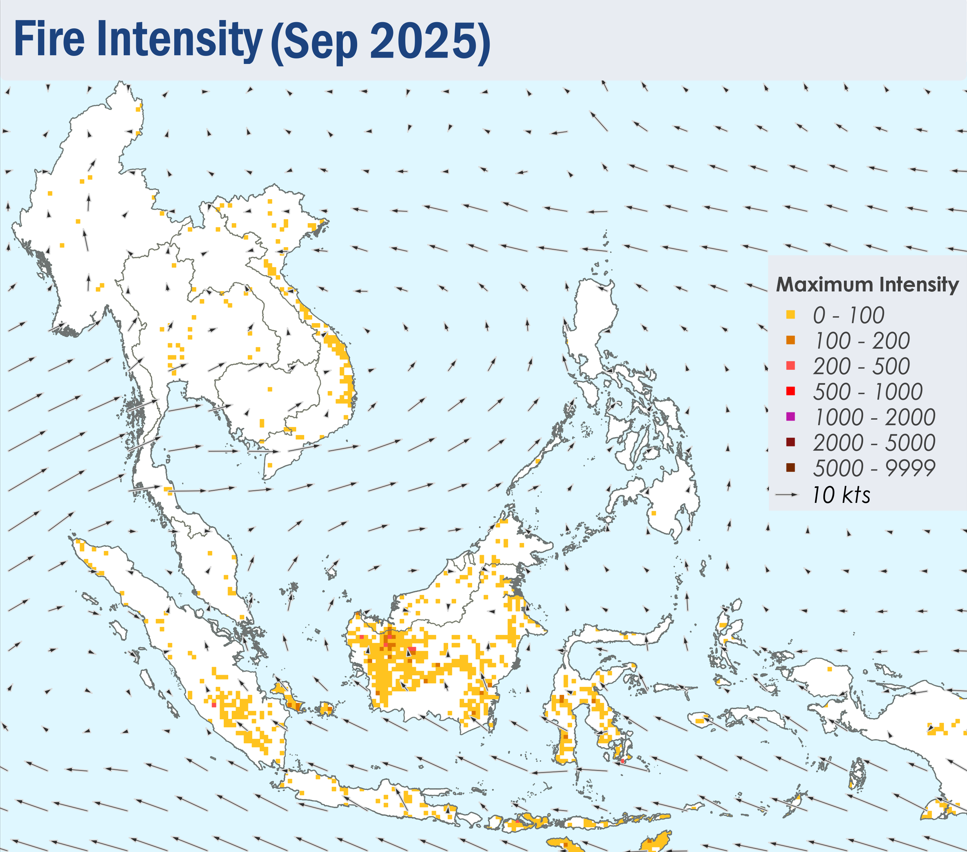
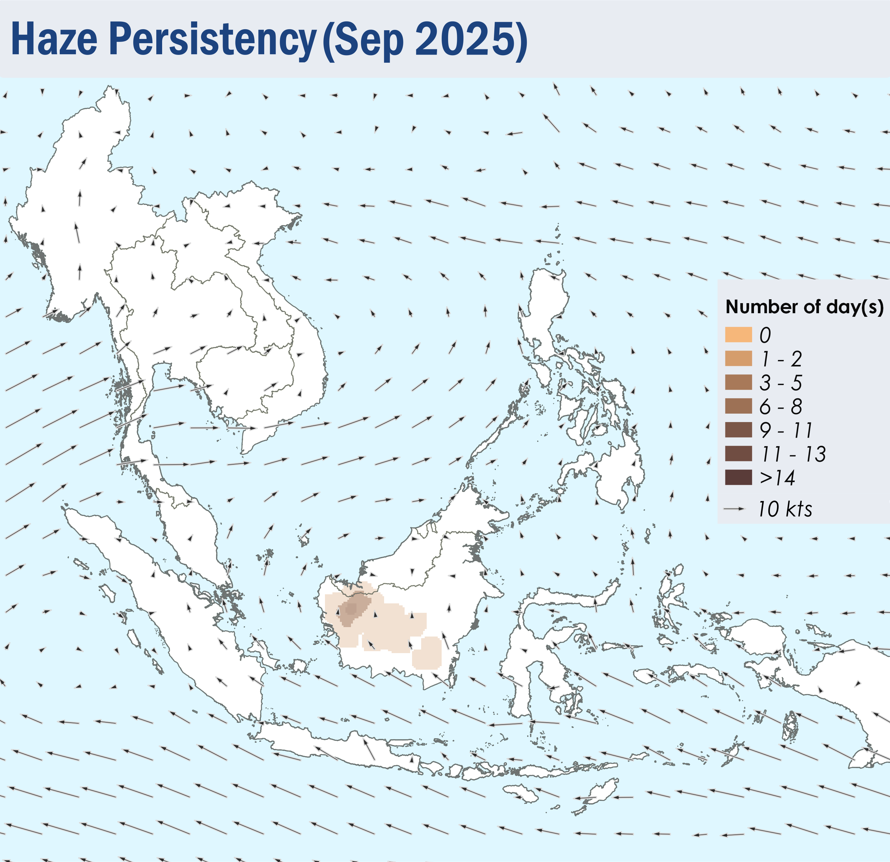
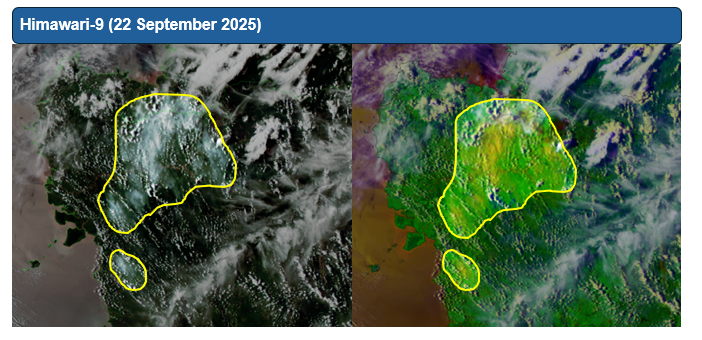
1.4 Isolated to scattered hotspots were detected in most parts of the southern ASEAN region, with persistent hotspot clusters detected in West Kalimantan, the southern parts of Sumatra, and the Lesser Sunda Islands (Figure 4). Hotspots were also detected as particularly intense in West Kalimantan and the Lesser Sunda Islands. Moderate smoke plumes were seen originating from hotspots in West and Central Kalimantan, with plumes from West Kalimantan occasionally drifting into western Sarawak (Figures 6 and 7). Slight localised smoke plumes were also noted in southern Sumatra on certain days. With the exception of isolated hotspots detected in parts of Viet Nam, hotspot and smoke haze activity over the northern ASEAN region remained subdued under the prevailing wet weather (Figure 4).